Networking is the foundation of every modern cloud architecture. With Amazon Web Services, organizations can leverage AWS Cloud Network Automation to simplify network configuration, improve efficiency, and ensure consistent performance across environments. AWS networking services are designed to securely connect applications, data, and users across regions, data centers, and edge locations. In addition, businesses can implement Edge AI Solutions with AWS to process data closer to the source, enabling faster insights and real-time decision-making. Whether supporting a small application or a global enterprise platform, AWS provides the tools to build reliable, scalable, and cost-optimized networks.
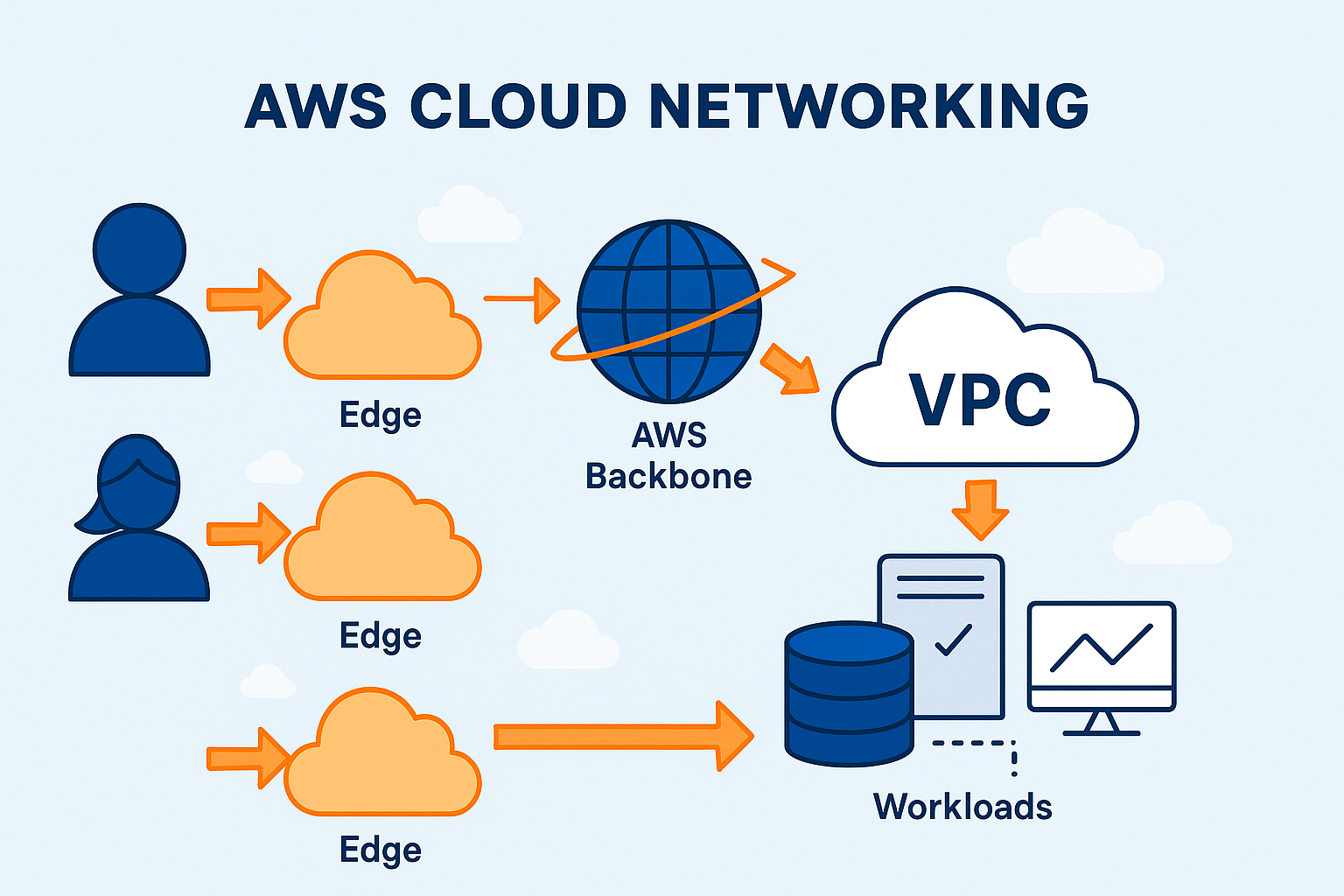
1. Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is the building block of AWS networking. It allows customers to create logically isolated networks within AWS, giving them full control over IP ranges, subnets, routing tables, and security boundaries.
- Subnets allow segmentation between public-facing and private resources.
- Security Groups and Network ACLs add multiple layers of traffic filtering.
- Features like VPC Peering and Transit Gateway connect multiple VPCs seamlessly.
This flexibility ensures workloads remain protected while still being able to communicate as needed.
2. Hybrid Connectivity
Many organizations operate in hybrid models combining existing on-premises systems with cloud workloads. AWS offers several ways to achieve secure connectivity:
- Site-to-Site VPN creates encrypted tunnels between on-premises data centers and AWS.
- AWS Direct Connect provides dedicated, high-bandwidth links for predictable performance and lower latency.
- AWS Cloud WAN simplifies management of global networks by centralizing policy and routing across multiple regions and locations.
These services make it possible to extend traditional networks into the cloud without disruption.
3. Application Traffic Management
High availability and performance depend on distributing traffic efficiently. AWS provides multiple services for this purpose:
- Elastic Load Balancing (ELB): Automatically distributes traffic across EC2 instances, containers, and IPs.
- Amazon Route 53: A global DNS service that routes users to the best endpoints based on latency, health, or geographic location.
- AWS Global Accelerator: Directs users to the nearest healthy AWS edge location using the AWS global backbone, reducing latency and improving reliability.
Together, these ensure that applications can serve global audiences without bottlenecks.
4. Content Delivery and Edge Networking
For organizations delivering digital content websites, media, APIs, or IoT data edge networking is critical.
- Amazon CloudFront: A global Content Delivery Network (CDN) that caches content at over 400+ edge locations, improving performance and reducing origin load.
- AWS Local Zones and Wavelength: Extend compute and networking services closer to end users for ultra-low latency use cases.
- IoT and Edge Gateways: Enable devices to connect securely and transmit data back to the cloud.
These services ensure users experience fast and consistent application performance no matter where they are located.
5. Security and Compliance in Networking
Security is deeply integrated into AWS networking. Key features include:
- Security Groups & NACLs: Fine-grained traffic controls at instance and subnet levels.
- AWS Network Firewall & WAF: Protection against common threats and malicious traffic.
- DDoS Protection (AWS Shield): Always-on mitigation against large-scale denial-of-service attacks.
- Encryption: Support for TLS, VPN encryption, and private connectivity ensures data confidentiality.
AWS also maintains compliance with global standards (ISO, SOC, HIPAA, GDPR), helping organizations meet regulatory requirements.
6. Edge AI Solutions with AWS
This allows you to explain how AWS brings AI/ML capabilities to the edge, mentioning SageMaker Edge Manager, IoT Greengrass, and Panorama, and tying it naturally to latency-sensitive applications and edge devices.
7. Monitoring and Observability
Understanding what happens within the network is vital for troubleshooting, optimization, and governance.
- Amazon CloudWatch: Provides monitoring, metrics, and alerts for resources.
- VPC Flow Logs: Capture traffic metadata for security analysis and auditing.
- AWS CloudTrail: Logs API activity to track changes to network configurations.
- AWS Network Manager: Centralizes network monitoring across regions and accounts.
These tools give organizations the visibility they need to maintain smooth operations.
8. Scalability and Global Reach
AWS networking is built on one of the world’s largest infrastructures, spanning multiple Availability Zones and Regions worldwide. Organizations can design:
- Multi-Region architectures for disaster recovery and compliance.
- Multi-VPC designs for environment separation and scaling.
- Global edge integrations for consistent application performance across continents.
This flexibility enables companies to scale from startups to multinational enterprises without redesigning their core networking.
AWS Cloud Networking is more than a collection of services it is the backbone that connects compute, storage, and applications into complete solutions. From isolated VPCs to global edge delivery, AWS provides the tools to build networks that are secure, reliable, and future-ready.
By leveraging these services, organizations can support modern applications, enable hybrid operations, and deliver faster, safer, and more consistent user experiences across the globe.